
Context:
The United States captured Venezuelan President Nicolás Maduro and took him out of the country on Saturday after an extraordinary nighttime operation that was accompanied by a flurry of strikes, following months of escalating pressure on the oil-rich South American nation.
Contents:
- Facts for Prelims
- Map of Venezuela
- Lake Maracaibo
- Heavy oil v/s Light oil
- Operation Just Cause v/s Operation Absolute Resolve
- OPEC
- Monroe Doctrine
- Why Maduro?
- Indian Govt. Stand on Maduro Arrest
- Impact on India
- Way forward
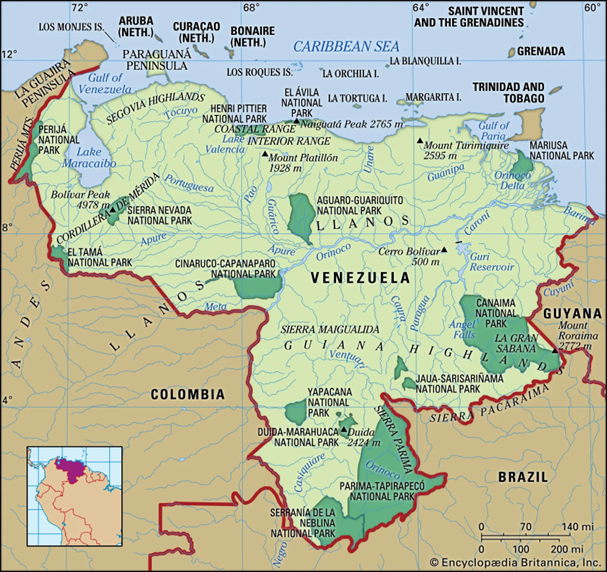
Venezuela
- Located in northern South America, along the Caribbean Sea
- Borders Colombia, Brazil, Guyana; strategic Caribbean location
- Features Andes Mountains (NW), Llanos plains, Guiana Highlands
- Home to Angel Falls (world’s highest waterfall)
- Orinoco River system crucial for drainage and economy
- Possesses one of the largest proven oil reserves globally.
Heavy oil v/s Light oil
- Venezuela is a member of the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC), a group of countries that largely dominates the global oil market. However, Venezuela currently produces a relatively small amount of crude oil compared with the other oil-producing nations.
- According to OPEC data, Venezuela accounts for about 3.5% of the OPEC’s total oil exports, and about 1% of global oil supplies.
- This relatively low supply is due to the U.S. sanctions on Venezuela and the heavy nature of Venezuelan oil.
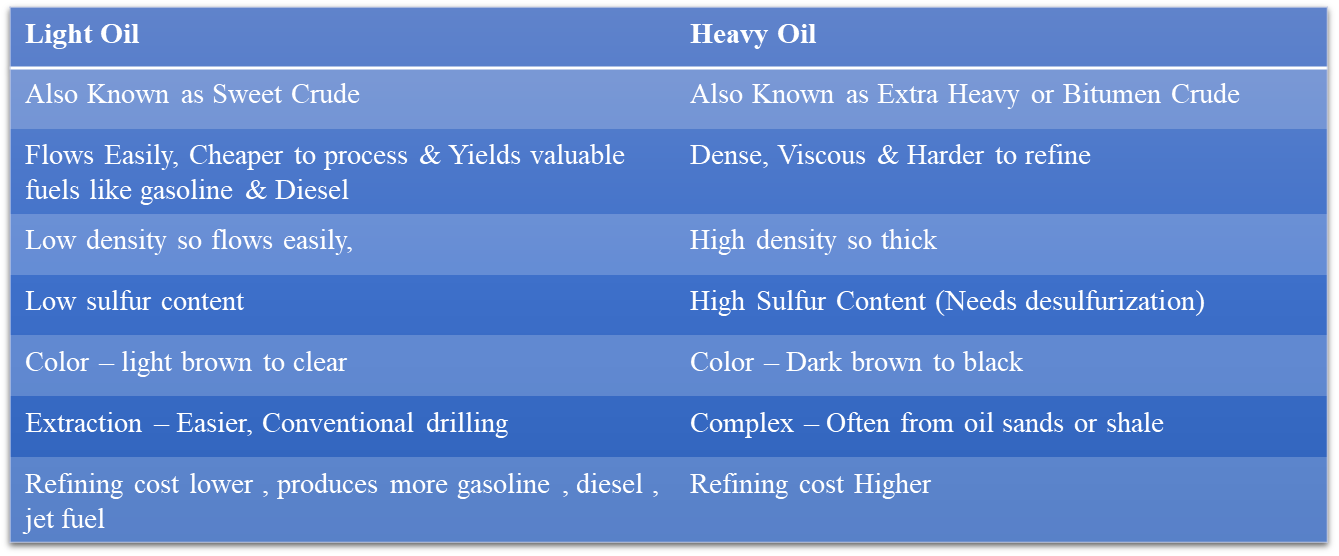
Note: Countries like Venezuela and Canada have vast heavy oil reserves, while the Middle East dominates light crude production.
Operation Just Cause v/s Operation Absolute Resolve
Operation Just Cause (1989) was the U.S. invasion of Panama to depose Manuel Noriega, while Operation Absolute Resolve (2026) was a large-scale U.S. strike to capture Venezuelan President Nicolás Maduro.
OPEC
- The OPEC is a permanent intergovernmental organization founded at the Baghdad Conference, in 1960 by Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, and Venezuela, headquartered in Vienna, Austria.
- OPEC currently has 12 members, including Algeria, Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Libya, Nigeria, Saudi Arabia, UAE, Congo, Gabon, Equatorial Guinea and Venezuela.
- OPEC nations produce about 30% of the world’s crude oil, hold 80% of proven reserves, and account for nearly half of global exports, with Saudi Arabia as the largest producer among the OPEC.
- World Oil Outlook report
OPEC+
- OPEC+ was formed in 2016 as an alliance between OPEC and 10 other oil producers to address declining oil prices due to US shale oil growth.
- Also Known as the Vienna Group.
- OPEC+ includes the OPEC members plus Azerbaijan, Bahrain, Brunei, Kazakhstan, Malaysia, Mexico, Oman, Russia, South Sudan, and Sudan.
- The OPEC and OPEC+ countries combined produce about 60% of global oil production.
Monroe Doctrine
- The Monroe Doctrine, announced in 1823 by U.S. President James Monroe, declared that the Americas were off-limits to further European colonization or interference.
- It became a cornerstone of U.S. foreign policy, asserting hemispheric dominance and later being invoked to justify interventions in Latin America, including the recent U.S. operation against Venezuela.
- Main idea:
Any attempt by European powers to colonize or interfere in the Western Hemisphere would be Viewed as a Hostile act against the United States. - Reciprocal Promise:
The U.S. pledged not to meddle in European affairs or existing colonies.
Why Maduro?
- Official reasons given by the USA:
- Narco-Terrorism Charges : Maduro & wife indictedd in NY on charges of narco-terrorism conspiracy + Cocain important conspiracy
- Regime Change Objective: Dismantling Maduro Govt; + Friendly Goverment.
- Humanitarian Framing: Claimed that the operation would liberate venezuelans from dictatorship;
Arguments given by Stanly Johny in his Article “Monroe Doctrine reloaded”
- According to Johny, one can point out at three broad reasons after carefully examining the most recent National Security Doctrine of the USA:
- Re-imposition of American Primacy in the Western Hemisphere.
- To keep China & Russia influence under check in the region.
- Oil
- Re-imposition of American Primacy in the Western Hemisphere.
- Reimposition of American primacy in the western hemisphere.
- US must deny space / influence or control by outside power in Latin America
- Western Hemisphere – must remain under American political economic & military influence.
- To keep China & Russia influence under check in the region.
- Keeping their influence in check
China – Huge investments in Latin America through BRI
– 24 signatories in the region
– Largest or 2nd Largest trading partner of most countries - China
– A/Cs for > 80% venezuela’s oil purchases
– Chinese CNPC : Largest foreign company with investments and operations in venezuela’s oil sector
- Keeping their influence in check
- Oil
- Venezuela – Holds about 17% of world’s known oil reserves (>300bn barrels (4x the reseves of US American Companies)
- Hugo Chavez (1999) – Nationalization of oil resources – (cause of heart burn)
- In December 2025 – Trump demanded venezuela to return all the ‘stolen American oil, Land & Assets’.
Indian Govt. Stand on Maduro Arrest
- In its statement issued on Sunday, calling the evolving situation in the South American country a matter of “deep concern”, the External Affairs Ministry did not refer to the United States or to the U.S. forces attacking the Venezuelan capital and taking Mr. Maduro captive, nor did it refer to UN principles.
- Russia, China, Brazil, South Africa, and others in the Global South condemned the U.S. action as a violation of international law.
- The government’s response was also in contrast to India’s response to a similar operation in 1989, when U.S. forces took Panamanian President Manuel Noriega captive and tried him in U.S. courts.In a speech in Parliament, then Foreign Minister I.K. Gujral had “deplored” the U.S. actions, invoking the UN charter and the principle of non-intervention.
Impact on India
Venezuelan crude accounted for about 0.3% of India’s total oil import in the current financial year up to November.
Given the low trade volumes, existing sanctions constraints, and the large geographical distance, the current developments in Venezuela are not expected to have any meaningful impact on India’s economy or energy security.
Implications for the World
- On International law & Sovereignty
- Violation of UN Charter – Art. 2(4) – All members shall refrain in their IR from the threat or use of force against the territorial integrity or pol. independency of any state.
- Setting a Wrong precedent that – Powerful nations may bypass international law to puesue regime change;
- Also goes against Nicaragua v/s USA (1984) – ICJ was considering the matter of the US using military force against the central America country .
Cold war +Contain Communism – However, Court held that action in response to those obj. was disproportionate & went against the sovereignty of Nicaragua
- On regional stability in Impact on India –
- Faces Political vacuum and Uncertainty
- Spillover effects – on refugees, economic disruption and posssible insurgencies
- Deepen mistrust of USA
- Geopolitical Fallout
- C+R+Cuba – Framed it as us imperialism
- Could accelerate multipolarity – Non-western power strengthening alliances to counter US unilateralism
- Risk of proxy conflicts – Venezuela may become a battleground for great power ….
- Energy & Economic Impact
- Holds some of the Largest oil reserves in the world
- Raises concerns about venezuelan oil exports, potentially reshaping global energy markets
- Global perception of the USA – Allies are uneasy – Al UNSC meeting held on 5th Jan. – Even Denmark questions this move
- L. American countries like Columbia – See it as a return to imperial – style interventions in LA;
Explore:👉Electoral Trusts: Who Donates, How Funds Flow, and Why It Matters
Question:
1. Catatumbo lightning is a natural phenomenon that occurs over the Catatumbo river in Chile;
2. Cirrus clouds are responsible for this phenomenon;
3. At its peak, it can cause almost average of 100 lightning strikes per minute;
Option:
a. 1 Statement is correct
b. 2 Statements are correct
c. All Statements are correct
d. All Statements are incorrect
- Catatumbo lightning is a mesmerizing natural phenomenon that occurs over the Catatumbo river in Venuzuela, where lightning strikes almost continuously.
- This phenomenon primarily happens at the mouth of the Catatumbo River, where it meets lake Maracaibo, the largest lake in Venezuela.
- A convergence of several factors gives rise to the unique conditions required for Catatumbo lightning.
- Warm, moist air from the Caribbean Sea is pushed towards the Andes mountains, where it collides with cooler air descending from the peaks.
- This collision creates a perfect storm of sorts, as the warmer air is forced to rise rapidly by the shape of the local landscape, and as it does, it cools and condenses, forming towering cumulonimbus clouds.
- Meanwhile, the combination of strong winds and temperature differentials generates electrical charges within these clouds.The cumulonimbus clouds – sometimes reaching heights of more than 5 km – load up on static electricity.
- When the electrical potential within the clouds becomes too great, it discharges in the form of lightning.
- Catatumbo lightning is distinguished by its frequency and duration: the strikes occur for up to 160 nights in a year, with an average of 28 lightning strikes per minute at its peak.
- Thanks to this constant flow of current, the area has earned the title of “the lightning capital of the world”.
Subscribe Our Youtube Channel: https://www.youtube.com/@CivilsPhodo






