
Introduction:
The recent escalation in the Middle East has once again captured global attention, as Israel strikes Iran in what is being described as a significant shift in regional dynamics. This military action marks a critical juncture in the long-standing tensions between the two nations, raising concerns over broader geopolitical implications. In this blog, we explore the background, reasons behind the Israeli airstrikes, and the potential consequences of this aggressive maneuver on regional stability, international diplomacy, and global security. Whether you’re following current affairs or preparing for UPSC or competitive exams, understanding the “Israel strikes Iran” issue is essential for deeper insight into modern international relations.
Context:
Early on Friday morning (13th June, 2025) in the Middle East, Israeli jets carried out dozens of strikes against nuclear and military sites in Iran. Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu called it “a targeted military operation to roll back the Iranian threat to Israel’s very survival,” adding that the operation would continue “for as many days at it takes to remove this threat.”
Content:
- Map of Middle-East
- Locations targeted
- What was JCPOA?
- Why Operation Rising Lion?
- What was the trigger: IAEA recent report
- Status of nuclear talks
- Way forward
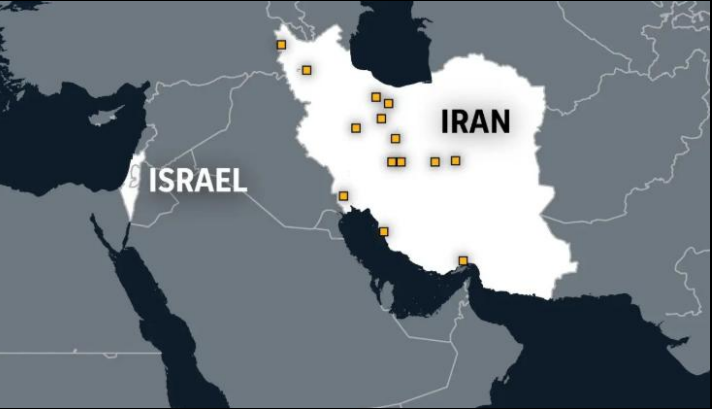
Locations targeted
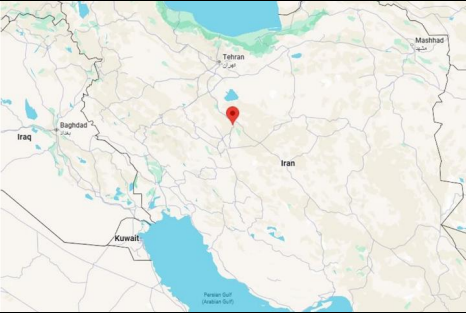
- Israel’s primary target was the Natanz Nuclear Facility,located in ISFAHAN Province in Central Iran.
- Natanz is the country’s main Uranium enrichment facility.
- Parchin Military Complex: Known for Missile Development and potential nuclear weapons research.
- Fordow Enrichment Facilities: located 90 meters underground near Qom.
- Mehrabad Airbase
- Residential areas (IRGC Linked)
Status of Nuclear talks
- Since April, the US and Iran have conducted five formal rounds of negotiations aiming for a deal which stops Iran from developing nuclear weapons in exchange for sanctions relief (This also suits America’s Rapprochement 2.0 policy).
- The biggest sticking point is not whether Iran has a right to nuclear energy but whether it can enrich uranium to fuel its nuclear power plants. (in theory it also allows it to produce a nuclear weapon with bomb grade 90% enriched Uranium.)
- So far, the US concession to Iran is to allow Tehran to enrich uranium temporarily, before delegating that right to a consortium of regional Arab states and itself which will then provide nuclear fuel to Iran.
- Iran has rejected this proposal, with Supreme Leader Ali Khamenei himself condemning it. Foreign Minister Abbas Araghchi on Tuesday asserted that his country does “not need anyone’s permission to enrich uranium” within its borders.
- But this has thus far been a red line for Washington, with Trump deeming Iran’s position “unacceptable”.
What is JCPOA?
- Also Known as Iran Nuclear Deal
- Signed in 2015 (with sunset clauses)
- After 10 Years, centrifuge restrictions to be removed
- After 15 years, limits on low enriched uranium to be removed.
- Parties to the deal: P5 + Germany + The European Union + Iran
Important Terms of JCPOA
- Provided Iran with sanctions relief in return for Tehran severely limiting the scope of its nuclear program.
- Restrictions on Iran:
- Not to enrich its uranium beyond 3.67%, a level suitable for peaceful nuclear power applications but not for weapons production.
- Signing a roadmap agreement with the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA).
Note: Trump unilaterally withdrew the US from the deal in 2018, during his first term as president.
Why Operation Rising Lion?
- The Israeli strikes followed months of heightened tensions between Israel and Iran, worsened by
- Previous Iranian attacks
- Nuclear concerns
- Immediate trigger
- Proxy conflicts
- Skepticism concerning US diplomacy
Implications of what exactly happened?
- Strategic Impact
- Escalation Risk
- Regional Dynamics
- US-Israel Tensions
Policy recommendations & strategic options
- Immediate de-escalation measures
- a) Backchannel Diplomacy: Leverage Oman’s established mediation role to facilitate direct U.S.-Iranian communication.
- b) Maritime Security Enhancement: Expand Operation Prosperity Guardian to include Gulf waters while maintaining defensive posturing.
- c) Regional Dialogue Framework: Establish multilateral forum including GCC states, Iraq, and Iran to address security concerns
Medium-term Strategic Adjustments
- Nuclear Negotiations Reset: Public opinion data suggesting American support for “a deal with Iran that limits its nuclear capabilities to peaceful ends” provides domestic political space for renewed diplomacy.
- Energy Security Diversification: Accelerate strategic petroleum reserve releases and alternative supply route development.
- Alliance Restructuring: Adapt U.S. regional partnerships to accommodate evolving Gulf state threat perceptions
Long-term Regional Architecture
- Consider Trump’s interest in “big, out-of-the-box deals” to pursue “denuclearization of the entire Middle East” as a framework for comprehensive regional security arrangements. This approach would require unprecedented diplomatic coordination but could address fundamental security dilemmas driving current tensions.
Scenario Analysis
- Limited Military Exchange
- Diplomatic Breakthrough
- Prolonged Tension without Direct Conflict
- Regional War
Way Forward
- Crisis resolution requires multiple actors to work together.
- The Trump administration’s willingness to engage in substantive nuclear negotiations,
- Israel’s restraint regarding unilateral military action, and
- Iran’s capacity to control proxy forces while maintaining strategic patience.
- Role of international communities particularly the roles of China, Russia, and European Powers.
- will be crucial in either facilitating de-escalation or managingthe consequences of military confrontation.
- Cyprus’s strategic positioning and India’s regional interests add complexity to potential crisis management scenarios.
- Ultimately, the current crisis underscores the urgent need for comprehensive regional security architecture that addresses nuclear proliferation concerns while accommodating legitimate security interests of all regional actors.
Conclusion
The “Israel strikes Iran” episode highlights the fragile balance of power in the Middle East. As tensions rise, the global community watches closely, hoping for diplomacy to prevail over further conflict.
Join Telegram Channel : UPSC with Deepak Prakash






