
Introduction
The implementation of Trump’s Reciprocal Tariff policy marked a significant shift in the global trade landscape, particularly affecting countries with substantial export relations with the United States. Designed to counter what the Trump administration perceived as unfair trade practices, the policy aimed to impose equal tariffs on imports from countries that levied higher duties on American goods. This move sparked widespread economic and political debate across the globe. In this context, understanding the impact of Trump’s Reciprocal Tariff on India and the rest of the world is crucial. The policy not only influenced bilateral trade dynamics but also had far-reaching consequences on global supply chains, international relations, and the overall structure of global trade norms.
In this blog post, we’ll explore the key provisions of Trump’s Reciprocal Tariff .
Context
- US President Donald Trump celebrated America’s “Liberation Day” on April 2 by announcing “reciprocal tariffs” against all major trading partners.
- Several countries with low per capita incomes have been hit by the highest tariffs.
- The tariffs will almost certainly have very significant economic consequences for the US and the rest of the world.
- There could be high inflation, slower growth, and worse.
Contents
- What is Reciprocal Tariff?
- What was announced?
- What was Smoot-Hawley Tariff Act, 1930?
- What about India?
- What about the rest of the World?
- Consequences of Trump Tariff
- Way Forward
What is Reciprocal Tariff?
- A Reciprocal Tariff is a tax or trade restriction that one country places on another country in response to similar actions taken by that country.
- The idea behind reciprocal tariffs is to create balance in trade between nations.
- Reciprocal tariffs can lead to a back-and-forth increase in trade barriers, potentially resulting in a trade war that negatively impacts both economies.
- Such situations can disrupt supply chains, raise prices for consumers, and slow down economic growth.
What was Announced?
There were two sets of Tariffs announced
1.Base tariff of 10% against all countries
- This in itself is a sharp increase from pre-Trump 2.0 tariff rate of around 2.5%
2.Country specific tariffs
- Arrived at by estimating how much each of these countries charges on US goods and then halving it to reach “USA discounted reciprocal tariffs”.
What was Smoot-Hawley Tariff Act, 1930?
- President Donald Trump’s tariff announcements have prompted a comparison with the Great Depression-era Smoot-Hawley Tariff Act, which ended up worsening the crisis it intended to resolve.
- In 1930, Congress passed a bill sponsored by Senator Reed Smoot of Utah and Rep. Willis Hawley of Oregon to raise import duties on 20,000 goods to protect American farmers and businesses.
Implications of Smoot-Hawley Tariff Act
- The Act spurred a trade war.
- Major trading partners, including Canada and Europe, retaliated with boycotts, quotas, and their own tariffs on American goods.
- American exports to retaliating nations fell by 28-32%.
- The Act jeopardized recovery efforts of countries trying to emerge from the impacts of World War I and the Great Depression.
- According to the Office of the US Historian, US imports from
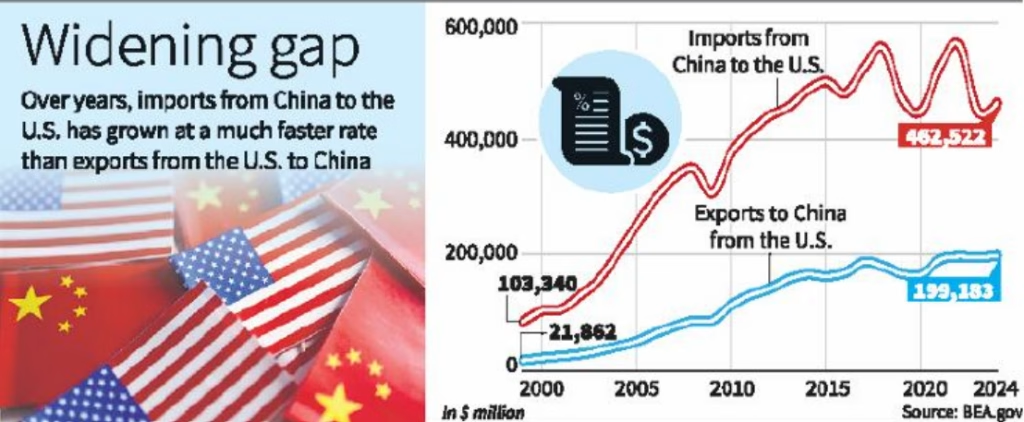
- Europe declined from a 1929 high of $1,334 million to just $390 million in 1932, while US exports to Europe fell from $2,341 million in 1929 to $784 million in 1932. Overall, world trade declined by 66% between 1929 and 1934.
Impact on India
The impact on India is playing out unevenly:
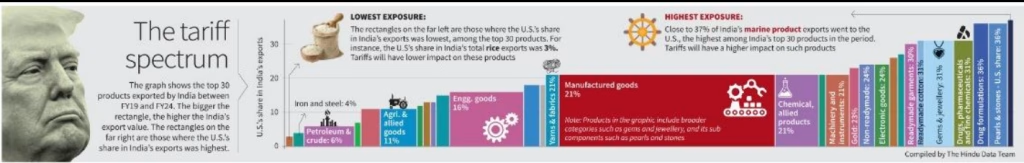
- Nearly $14 billion worth of electronics products and over $9 billion worth of gems and jewellery are among the top sectors to be hit by the U.S. tariffs.
- While the 26% tariff will not apply to auto parts and aluminium products, those will still attract the 25% tariff that Trump had announced earlier.
- pharmaceutical products and energy products are exempt under the latest round of tariffs.
- Marine sector going to be hit hard.
What about the rest of the world?
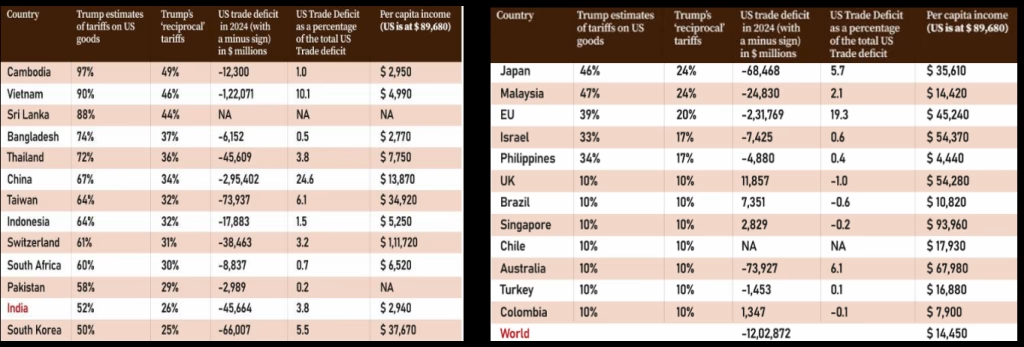
- Cambodia — with a per capita income of just $2,950 (just a tad more than India) and accounting for just 1% of the overall US trade deficit — has been hit with the highest level of tariffs.
- Bangladesh — with an even lower per capita income and accounting for half a per cent of the overall US trade deficit — has got a tariff of 37%
- In contrast, China (with a much higher per capita income and accounting for almost 25% of the total US deficit) and the EU (with an even higher per capita income and accounting for almost 20 per cent of US trade deficit) have been hit with 34% and 20% tariffs respectively.
Consequences of Trump Tariff
- Douglas Irwin, a professor of economics at Dartmouth and author of Clashing over Commerce: A History of US Trade Policy (2017), told Bloomberg that Trump’s tariffs would be “much bigger than Smoot-Hawley” due to the scale of today’s trade, with US imports amounting to 14% of its GDP, three times the share in 1930.

- Slower growth in the US:
- In case no country retaliates: stock market then also will fall to reflect lower profit outlook
- In case retaliations take place.
- Higher inflation in the US Stagflation and its political fallout: If growth falters and inflation spikes
- High inflation and slower growth elsewhere
Way Forward
- Learn from History: Smoot-Hawley Tariff Impact
- Other countries should also address Trump concern
- Would affect America’s interest in the long term: Rapprochement 2.0
- Trump should try to address tariff related issue.
Conclusion
Trump’s Reciprocal Tariff policy reshaped global trade by challenging existing norms and triggering tariff tensions. Its impact on India and other nations highlighted the vulnerabilities of export-dependent economies and underscored the need for balanced, fair trade practices in a rapidly evolving global market.
Join Our Telegram Channel : UPSC With Deepak Prakash






